Modern mobile apps and websites allow users to upload profile pictures and other files. Handling file upload is a common requirement while building a REST API with Node.js & Express.
In this tutorial, we will go discuss how to handle single and multiple file uploads with Node.js and Express backend and save uploaded files on the server.
Installation
First, let us create a new Node.js app by running the below commands. I am using npm for package management. It should be fine to use yarn if you like.
# creat a new directory & switch to it
$ mkdir files-upload && cd files-upload
# run this for npm to create a new app
$ npm init -y
# run this for yarn to create a new app
$ yarn init -y
-y or --yes skips the interaction session and generates a package.json file based on your defaults.
Next, run the following command to install the required dependencies:
# run this for npm
$ npm install express body-parser cors express-fileupload morgan lodash --save
# or using yarn
$ yarn add express body-parser cors express-fileupload morgan lodash
Here is what each of the above packages does:
express- Popular web framework built on top of Node.js. We shall use it for developing REST API.body-parser- Node.js request body parsing middleware parses the incoming request body before your handlers and makes it available under thereq.bodyproperty. In short, it simplifies incoming requests.cors- Another Express middleware for enabling CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) requests.express-fileupload- Simple Express middleware for uploading files. It parsesmultipart/form-datarequests, extracts the files if available, and makes them available under thereq.filesproperty.morgan- Node.js middleware for logging HTTP requests.lodash- A JavaScript library that provides utility functions for arrays, numbers, objects, strings, etc.
Create Express Server
After installing the required dependencies, let us start creating our Express server.
index.js
const express = require('express');
const fileUpload = require('express-fileupload');
const cors = require('cors');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const morgan = require('morgan');
const _ = require('lodash');
const app = express();
// enable files upload
app.use(fileUpload({
createParentPath: true
}));
//add other middleware
app.use(cors());
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: true}));
app.use(morgan('dev'));
//start app
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(port, () =>
console.log(`App is listening on port ${port}.`)
);
The above code is straightforward. First, it setups the express-fileupload middleware to enable multipart/form-data requests. Afterward, other Express middleware are added to allow Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS), request body parsing, and HTTP request logging. In the end, it starts the server at port 3000.
Upload Single File
Let us create our first route to allow users to upload their profile pictures.
app.post('/upload-avatar', async (req, res) => {
try {
if(!req.files) {
res.send({
status: false,
message: 'No file uploaded'
});
} else {
//Use the name of the input field (i.e. "avatar") to retrieve the uploaded file
let avatar = req.files.avatar;
//Use the mv() method to place the file in the upload directory (i.e. "uploads")
avatar.mv('./uploads/' + avatar.name);
//send response
res.send({
status: true,
message: 'File is uploaded',
data: {
name: avatar.name,
mimetype: avatar.mimetype,
size: avatar.size
}
});
}
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).send(err);
}
});
The above code snippet is an HTTP POST function. When you send a multipart/form-data request to the /upload-avatar route to upload a file, this function saves the file to the uploads folder on the server.
How does express-fileupload middleware work?
It makes the uploaded files accessible from the req.files property. For example, if you are uploading a file called my-profile.jpg, and your field name is avatar, you can access it via req.files.avatar. The avatar object will contain the following information:
avatar.name- The name of the uploaded file i.e.my-profile.jpgavatar.mv- The function to move the file elsewhere on the serveravatar.mimetype- The mime-type of the fileavatar.size- The size of the file in bytesavatar.data- A buffer representation of the uploaded file
Upload Multiple Files
Let us start creating another route to allow users to upload multiple photos in one request.
app.post('/upload-photos', async (req, res) => {
try {
if(!req.files) {
res.send({
status: false,
message: 'No file uploaded'
});
} else {
let data = [];
//loop all files
_.forEach(_.keysIn(req.files.photos), (key) => {
let photo = req.files.photos[key];
//move photo to uploads directory
photo.mv('./uploads/' + photo.name);
//push file details
data.push({
name: photo.name,
mimetype: photo.mimetype,
size: photo.size
});
});
//return response
res.send({
status: true,
message: 'Files are uploaded',
data: data
});
}
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).send(err);
}
});
The above code is relatively similar to a single file upload, except that we now receive a field photos instead of avatar. We used lodash utility functions ( _.forEach() & _.keysIn()) to loop over the photos field and save each photo to uploads directory.
Testing the Application
We're almost done! Run the following command in your terminal from the root directory of the project to start the application:
$ node index.js
It will start the application at port 3000. Let us use Postman for sending HTTP multipart/form-data requests:
1. Single File
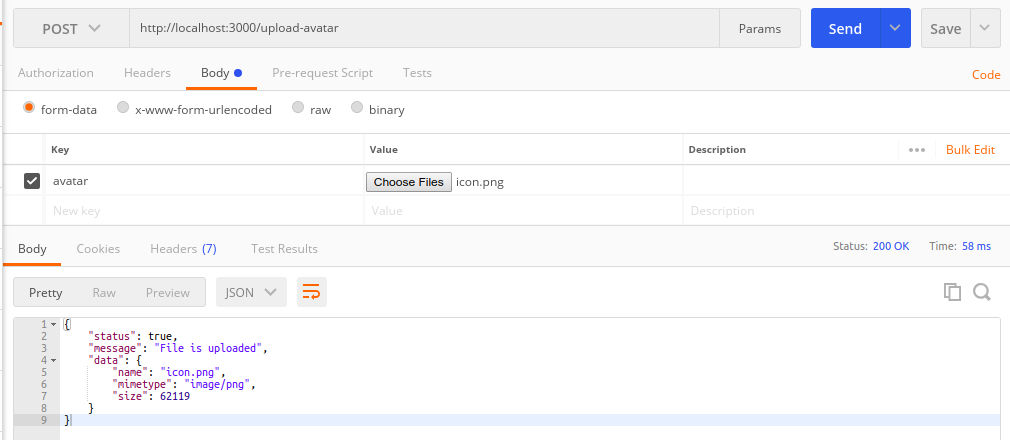
2. Multiple Files
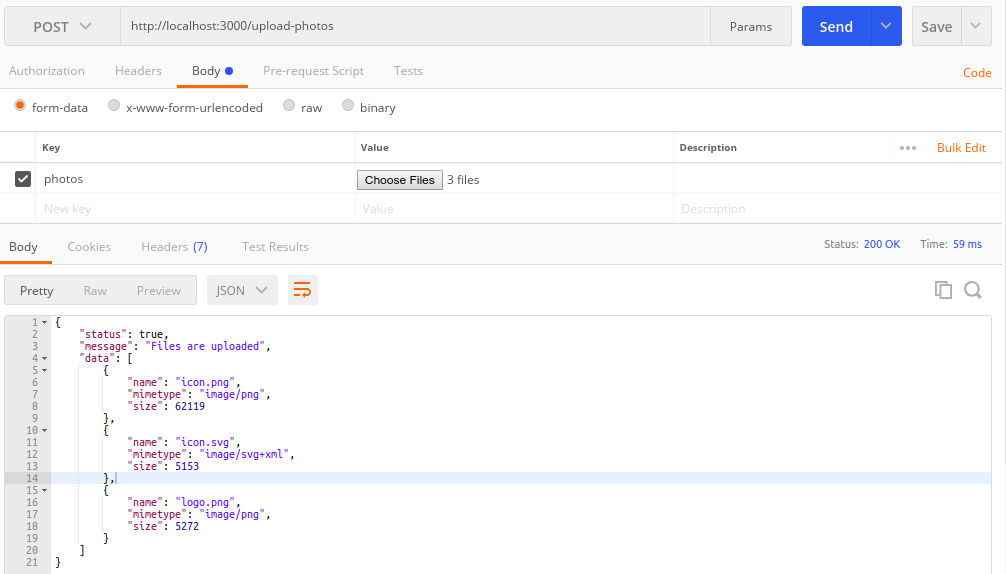
If you want to make the uploaded files publicly accessible from anywhere, just make the uploads directory static:
app.use(express.static('uploads'));
Now, you can open the uploaded file directly in the browser:
http://localhost:3000/icon.png
File Size Limit
If you want to limit the size of the files uploaded at once, pass the limits options directly to the express-fileupload middleware:
app.use(fileUpload({
createParentPath: true,
limits: {
fileSize: 2 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 //2MB max file(s) size
},
}));
Source code: Download the complete source code from GitHub available under MIT license.
Conclusion
That's all folks! We learn how to upload single and multiple files using Node.js and the Express framework. The express-fileupload library is an easy-to-use Express middleware for handling file(s) upload. Read its documentation for more configuration options.
Read Next: Express File Upload with Multer in Node.js
✌️ Like this article? Follow me on Twitter and LinkedIn. You can also subscribe to RSS Feed.