In an earlier article, I wrote about how to map a many-to-many entity relationship using Spring Data JPA and MySQL in a Spring Boot project. We created a join table to hold the primary keys of both relationship tables. These keys act as a composite primary for the join database table.
Simply put, a composite primary key, also known as a composite key, is a key that contains two or more columns to form a primary key for the table.
In this article, you'll learn how to map a composite primary key in a Spring Boot project using Spring Data JPA's both @IdClass and @EmbeddedId annotations.
Mapping Composite Key using @IdClass Annotation
Let us consider an application that manages different types of bank accounts. Each bank account has an account number and type (checking or saving), among other information. We want to create a compound key using this information to uniquely identify each account in the database.
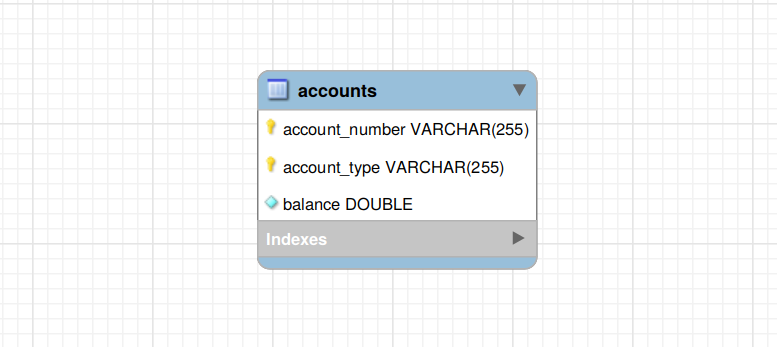
In the above Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram, the accounts table has a composite primary key, which consists of two columns:
account_numberaccount_type
To map this database relationship using Spring Data JPA, we need to create a separate composite primary key class with both these primary key columns:
AccountId.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Objects;
public class AccountId implements Serializable {
private String accountNumber;
private String accountType;
public AccountId() {
}
public AccountId(String accountNumber, String accountType) {
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
this.accountType = accountType;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
AccountId accountId = (AccountId) o;
return accountNumber.equals(accountId.accountNumber) &&
accountType.equals(accountId.accountType);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(accountNumber, accountType);
}
}
Note: The composite primary key class must be public, contains a no-argument constructor, defines both
equals()andhashCode()methods, and implements theSerializableinterface.
The next step is to create an Account entity class that declares all attributes of AccountId and annotates them with the @Id annotation:
Account.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.IdClass;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name = "accounts")
@IdClass(AccountId.class)
public class Account implements Serializable {
@Id
private String accountNumber;
@Id
private String accountType;
private double balance;
public Account() {
}
public Account(String accountNumber, String accountType, double balance) {
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
this.accountType = accountType;
this.balance = balance;
}
// getters and setters, equals(), toString() .... (omitted for brevity)
}
As you can see above, we have annotated the Account class with @IdClass to specify a composite primary key class that is mapped to multiple fields of the entity. The @Id annotation is then used to indicate all properties which are a part of the compound key.
With the @IdClass annotation, you can easily query data without using the name of the composite key class. Let us first create a repository interface for this purpose:
AccountRepository.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.repositories;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.Account;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.AccountId;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface AccountRepository extends CrudRepository<Account, AccountId> {
// TODO: add queries
}
Here is how you can write a simple derived query to fetch all bank accounts by a given account type:
List<Account> findByAccountType(String accountType);
Mapping Composite Key using @EmbeddedId Annotation
In additional to @IdClass, Spring Data JPA provides another annotation — @EmbeddedId — to define a composite primary key.
Let us consider another example application that manages employees of a company with multiple departments. Each employee has a unique ID within their own department. But the same ID can be assigned to a different employee in another department. So we cannot uniquely identify an employee just by his employee ID.
To uniquely identify an employee, we need to know his employee ID and his department ID. As you can see in the below Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram, the employees table contains a composite primary key that includes both employee_id and department_id columns:
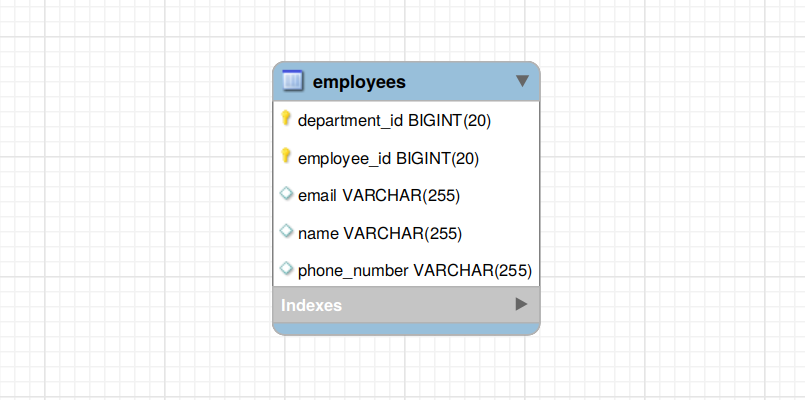
To map the above relationship using Spring Data JPA, you need to create a separate composite primary key class annotated with @Embeddable:
EmployeeId.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Embeddable;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Objects;
@Embeddable
public class EmployeeId implements Serializable {
@Column(name = "employee_id")
private Long employeeId;
@Column(name = "department_id")
private Long departmentId;
public EmployeeId() {
}
public EmployeeId(Long employeeId, Long departmentId) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
this.departmentId = departmentId;
}
public Long getEmployeeId() {
return employeeId;
}
public void setEmployeeId(Long employeeId) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
}
public Long getDepartmentId() {
return departmentId;
}
public void setDepartmentId(Long departmentId) {
this.departmentId = departmentId;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
EmployeeId that = (EmployeeId) o;
return employeeId.equals(that.employeeId) &&
departmentId.equals(that.departmentId);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(employeeId, departmentId);
}
}
The next step is to create the Employee class and embed the above composite primary class into it by using the @EmbeddedId annotation:
Employee.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.EmbeddedId;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee implements Serializable {
@EmbeddedId
private EmployeeId employeeId;
private String name;
@Column(unique = true)
private String email;
private String phoneNumber;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(EmployeeId employeeId, String name, String email, String phoneNumber) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
// getters and setters, equals(), toString() .... (omitted for brevity)
}
In the above Employee class, we have specified the composite key class using the @EmbeddedId annotation and marked it as a primary key of the entity.
Next, create a repository interface for retrieving Employee entities from the database, as shown below:
EmployeeRepository.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.repositories;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.Employee;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.EmployeeId;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends CrudRepository<Employee, EmployeeId> {
// TODO: add queries
}
Let us create another derived query to fetch all employees by a given department ID:
List<Employee> findByEmployeeIdDepartmentId(Long departmentId);
Testing Composite Primary Key Mapping
Finally, let us create the main application class to test the composite primary key mapping:
Application.java
package com.attacomsian.jpa;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.Account;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.AccountId;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.Employee;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.domains.EmployeeId;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.repositories.AccountRepository;
import com.attacomsian.jpa.composite.repositories.EmployeeRepository;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner mappingDemo(AccountRepository accountRepository,
EmployeeRepository employeeRepository) {
return args -> {
// ======= `@IdClass` Annotation =======
// create new accounts
accountRepository.save(new Account("458666", "Checking", 4588));
accountRepository.save(new Account("458689", "Checking", 2500));
accountRepository.save(new Account("424265", "Saving", 100000));
// fetch accounts by a given type
List<Account> accounts = accountRepository.findByAccountType("Checking");
accounts.forEach(System.out::println);
// fetch account by composite key
Optional<Account> account = accountRepository.findById(new AccountId("424265", "Saving"));
account.ifPresent(System.out::println);
// ======= `@EmbeddedId` Annotation =======
// create new employees
employeeRepository.save(new Employee(new EmployeeId(100L, 10L),
"John Doe", "john@example.com", "123456"));
employeeRepository.save(new Employee(new EmployeeId(101L, 20L),
"Emma Ali", "emma@example.com", "654321"));
// fetch employees by a given department id
List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findByEmployeeIdDepartmentId(20L);
employees.forEach(System.out::println);
// fetch employee by composite key
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeRepository.findById(new EmployeeId(100L, 10L));
employee.ifPresent(System.out::println);
};
}
}
In the main application class, we used both AccountRepository and EmployeeRepository repositories to test our implementation of a composite primary key with @IdClass and @EmbeddedId.
The next step is to run the application to see the output. For Gradle, execute the following command to start the application:
$ ./gradlew bootRun
For Maven, type the following command to launch the application:
$ ./mvnw spring-boot:run
When the application starts, you should see the following output printed on the console:
Account{accountNumber='458666', accountType='Checking', balance=4588.0}
Account{accountNumber='458689', accountType='Checking', balance=2500.0}
Account{accountNumber='424265', accountType='Saving', balance=100000.0}
Employee{employeeId=EmployeeId{employeeId=101, departmentId=20}, name='Emma Ali', email='emma@example.com', phoneNumber='654321'}
Employee{employeeId=EmployeeId{employeeId=100, departmentId=10}, name='John Doe', email='john@example.com', phoneNumber='123456'}
@IdClass vs @EmbeddedId
The main difference between @IdClass and @EmbeddedId annotations is that with @IdClass, you need to specify the primary key columns twice — once in the composite primary key class and then again in the entity class with the @Id annotation.
The @EmbeddedId annotation is more verbose than @IdClass as you can access the entire primary key object using the field access method. This also gives a clear notion of the fields part of the composite key because they are all aggregated in a class that is only accessible through a field access method.
Another difference between @IdClass and @EmbeddedId is when it comes to creating custom JPQL queries.
For example, with @IdClass, the query is a little simpler:
SELECT a.accountType FROM Account a
With @EmbeddedId, you have to write more text for a similar query:
SELECT e.employeeId.departmentId FROM Employee e
The @IdClass annotation can be a preferred choice over @EmbeddedId in situations where the composite primary key class is not accessible or comes in from another module or legacy code. For scenarios where you cannot modify the composite key class, the @IdClass annotation is the only way out.
Source Code: Download the complete source code from GitHub available under MIT license.
Conclusion
That's all for handling a composite primary key mapping using Spring Data JPA's @IdClass and @EmbeddedId annotations. You've learned about two different approaches to working with compound keys.
We've also discussed the differences between the @IdClass and the @EmbeddedId annotations. If we need to access parts of the composite key, just use @IdClass, but for scenarios where you frequently use the composite key as an object, @EmbeddedId should be preferred.
Don't forget to subscribe for updates if you want to be the first to know when new tutorials are available.
Further Reading
To learn more about Spring Data JPA, check out the following articles:
- Getting Started with Spring Data JPA
- Spring Data JPA with H2 DataBase and Spring Boot
- Accessing Data with Spring Data JPA and MySQL
- Derived Query Methods in Spring Data JPA
- Spring Data JPA Custom Queries using @Query Annotation
- How to Use Spring Data JPA Named Queries
- Sorting Query Results in Spring Data JPA
- Pagination with Spring Data JPA
- Spring Data JPA One To One Relationship Mapping Example
- Spring Data JPA One To Many Relationship Mapping Example
- Spring Data JPA Many To Many Relationship Mapping Example
- Introduction to Spring Data JPA Repositories
✌️ Like this article? Follow me on Twitter and LinkedIn. You can also subscribe to RSS Feed.